Warning
You are reading the documentation for an older Pickit release (2.4). Documentation for the latest release (4.0) can be found here.
Tool models and flexible pick orientation
In practice, many tools can tolerate some variation with respect to the nominal pick orientation without compromising pick success. Taking advantage of this can increase the likelihood that a pick point is pickable by the robot. This variation is typically due to:
Robot tool compliance, such as flexible suction cup bellows (below left).
Application-specific constraints, like the clearance between the tool fingers and the object at the pick point (below right).
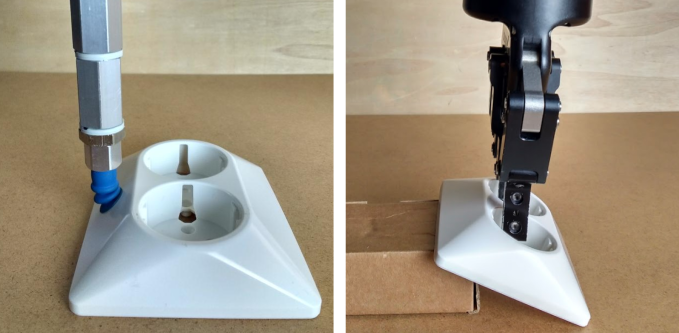
This article describes the features provided by Pickit to model such flexible pick orientation.
Flexible orientation at the pick point
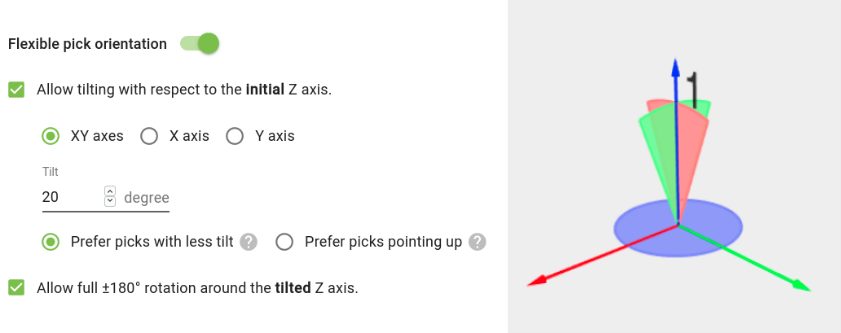
Most tool models allow setting the optional Flexible pick orientation, which specifies the orientation flexibility allowed at the pick point.
Pickit allows the pick orientation to tilt around the X and/or Y axes, as well as to rotate around the tool Z-axis (below left). Flexibility around each axis is represented as a circular sector as wide as the specified interval size (below right). It can be visualized in the robot tool and pick point views.
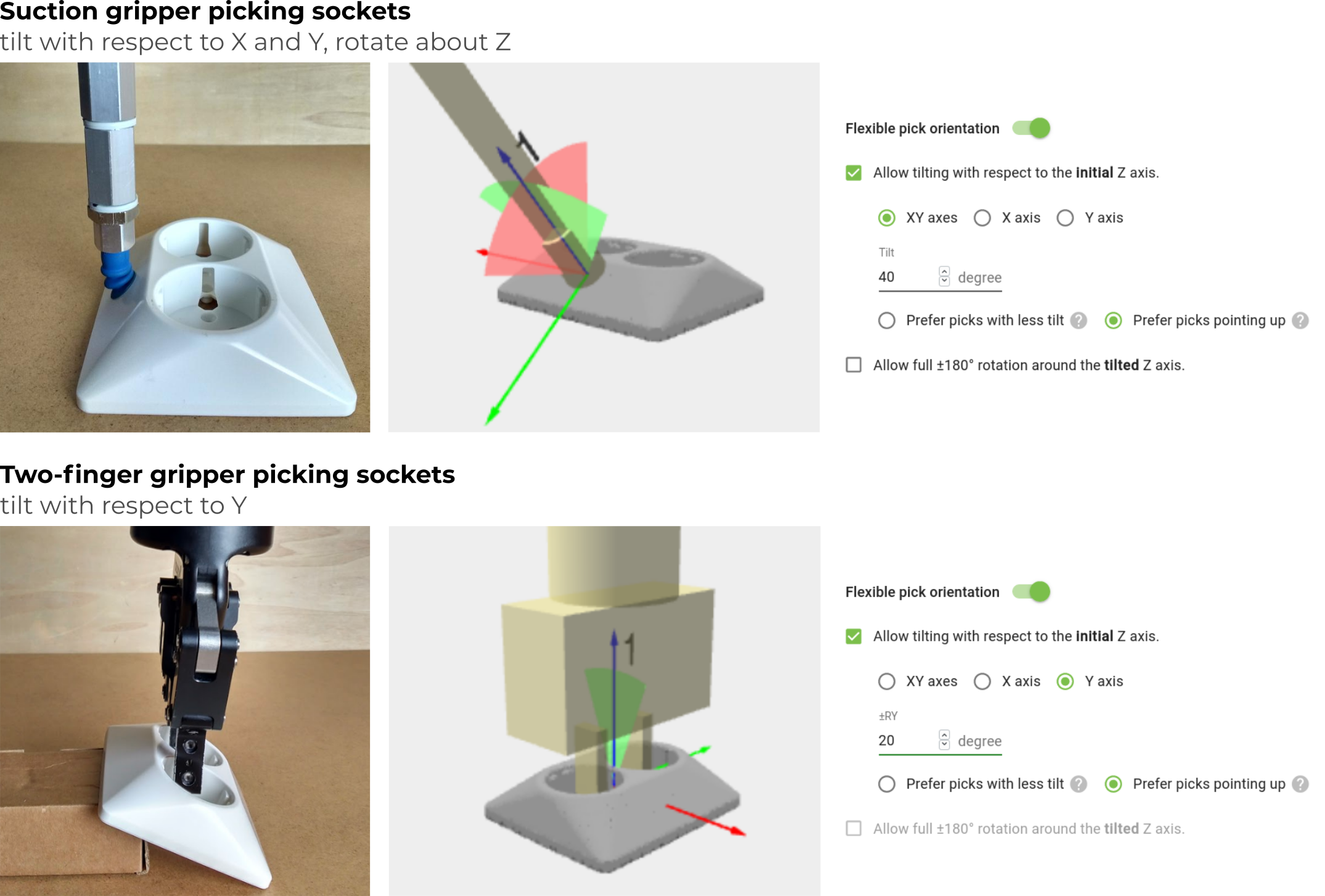
The following examples show, from left to right:
A picture of the real application.
The 3D visualization of the object model, robot tool model, pick point, and flexible pick orientation.
The flexible pick orientation specification.
It’s possible to instruct Pickit how much we want the tool to use its tilt flexibility:
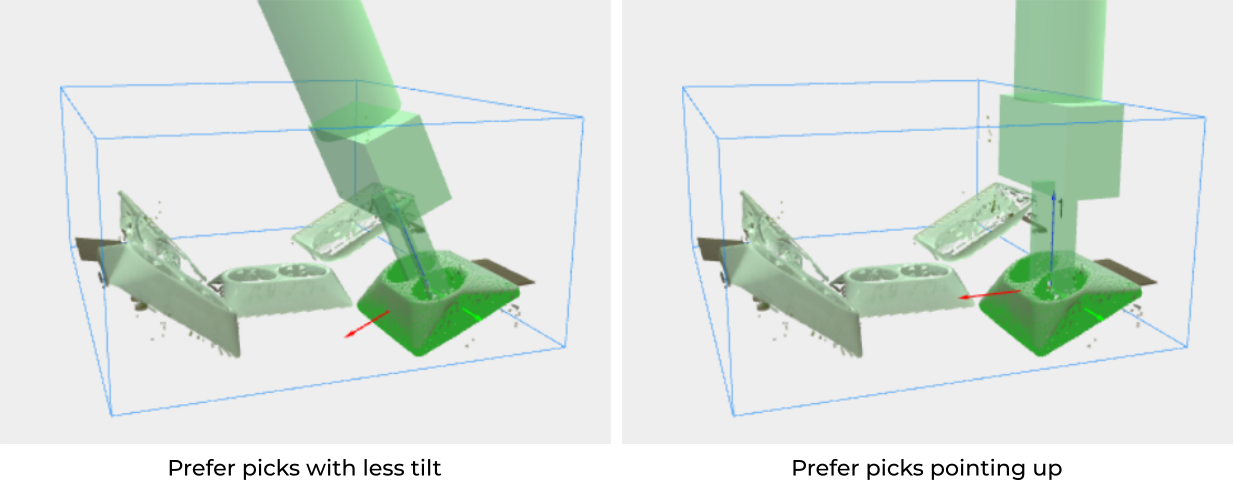
When Prefer picks with less tilt is selected, the tilting flexibility will only be used to make a point pickable, such as to avoid a collision between the robot tool and the bin or other objects. If apart from tilting, the tool additionally allows rotating about the Z-axis, this rotation will be used to align as close as possible to the preferred pick orientation. This is the default setting, and is recommended whenever tilting the tool decreases the likelihood of pick success. For instance, some suction cups might have more difficulty establishing vacuum when highly tilted.
On the other hand, when Prefer picks pointing up is selected, the tilting flexibility will be used to align as much as possible with the preferred pick orientation, which points up. The real application pictures shown above correspond to this situation. Prefer this setting when you want to minimize tilting of the robot flange.
The below image shows the difference between the two alternatives for a gripper allowed to tilt 30°.
Tip
Apart from the flexible pick orientation of the robot tool model, multiple pick points and pick point symmetry axes are other strategies for increasing the likelihood of an object being pickable.
Tip
Flexible pick orientations, in combination with the preferred pick point orientation can be used to favor picks that are easier and faster to reach by the robot (e.g. less wrist motion, lower occurrence of unreachable points).